Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon- Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari General de Catalunyaen/health-centers/hospital-universitari-general-catalunya
 Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
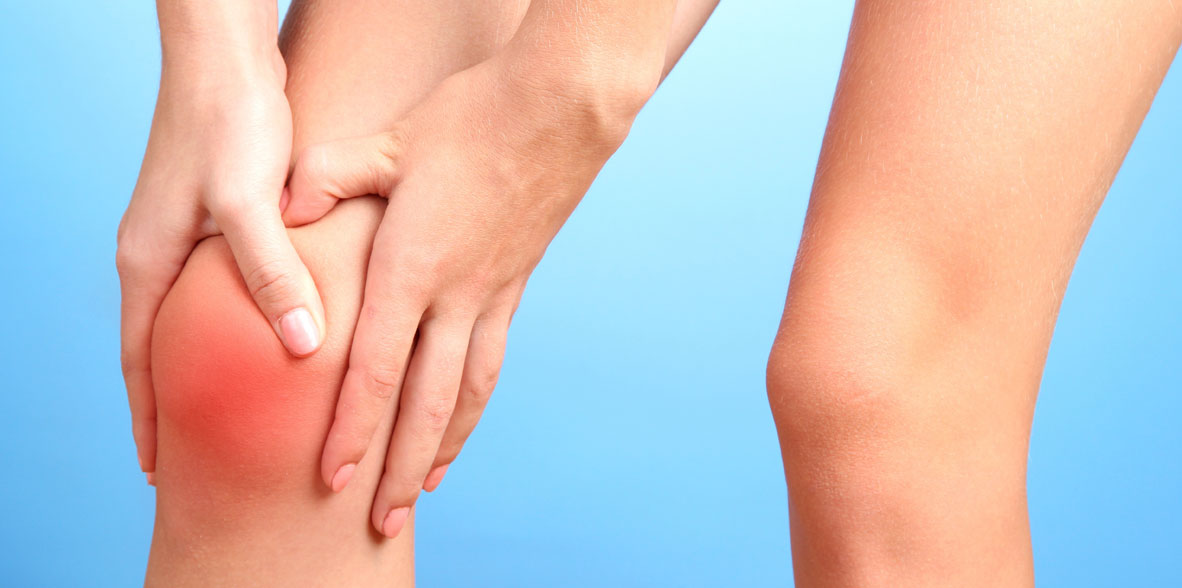
Anserine bursitis is an inflammation of the anserine bursa, a fluid-filled bursa located on the inside of the knee below the hamstring. The bursa acts as a cushion between the bones, muscles, and tendons found in the knee area. Anserine bursitis usually results from chronic irritation of the bursa, which may be due to repetitive overuse of the area, traumatic injury, infection, or chronic inflammatory disease such as arthritis.
Symptoms of anserine bursitis include pain and tenderness in the inner knee area, as well as localized swelling and redness. The pain is usually worse when bending or straightening the knee, or when walking or running on hard surfaces. In some cases, anserine bursitis can be mistaken for other knee problems, such as a meniscus injury or ligament injury.
Treatment of anserine bursitis depends on the severity of symptoms. Some treatment options include:
- It is important to avoid any activity that aggravates the symptoms of anserine bursitis, such as running or jumping. Resting and limiting activity can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Specific stretching and strengthening exercises may be prescribed to help relieve the symptoms of anserine bursitis, as well as other physical therapy techniques to reduce inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and pain in the affected area.
- In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and pain.
- In very rare cases, anserine bursitis may be caused by infection. In these cases, aspiration of the bursa may be performed to remove the infected fluid.