Morgenstern López Rudolf
- Our services
Who is eligible for endoscopic cervical fusion surgery?
Cervical pain and/or radiated pain into the arms is caused in most cases by disk herniations and foraminal stenosis that can usually be solved by endoscopic surgery.  However, there are also cases for which it is necessary to place implants and disk spacers/cages into de cervical disk. Endoscopic cervical spine fusion surgery is indicated for cases with more complex cervical pathologies, like cervical instability (spondilolysthesis), deformity of the cervical spine (kyphosis) and bialteral radiating arm pain.
However, there are also cases for which it is necessary to place implants and disk spacers/cages into de cervical disk. Endoscopic cervical spine fusion surgery is indicated for cases with more complex cervical pathologies, like cervical instability (spondilolysthesis), deformity of the cervical spine (kyphosis) and bialteral radiating arm pain.
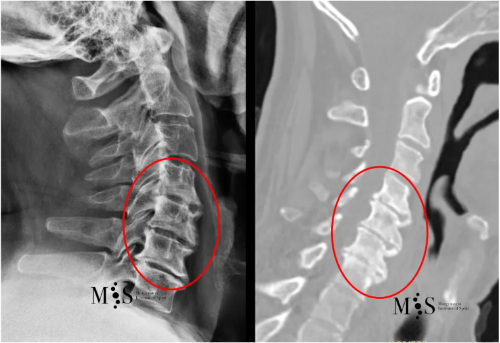
CT Scan (right) and X-ray film (left) of a cervical spine with advanced
degeneration of the cervical interbody disks (marked by a red circle).
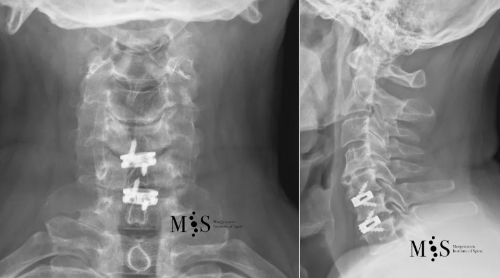
Post-operative X-rays showing an interbody cage at two separate cervical disks after placement with endoscopic fusion surgery
of the cervical spine and was discharged from the hospital in less than 24 hours after surgery.
Dr. Morgenstern is a wordl-wide pioneer in the development of endoscopic anterior cervical fusion surgery (endoACDF) that allows the placement of an interbody cage into a disk of the cervical spine using only a small skin incision of just 2 cm length at the patient’s throat.
Endoscopic anterior fusion surgery is performed with progressive tissue dilation and does NOT require wide dissection of anatomic structures at the patient’s throat. Hence, risk of scar tissue formation and bleeding is considerably reduced consequenlty also decreasing the risk for infection, hematoma, etc. Therefore, endoscopic ACDF surgery does NOT require monitoring in the ICU and the patient can be discharged from the hospital in less than 24 hours after surgery.
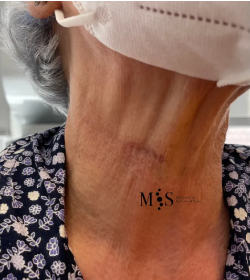
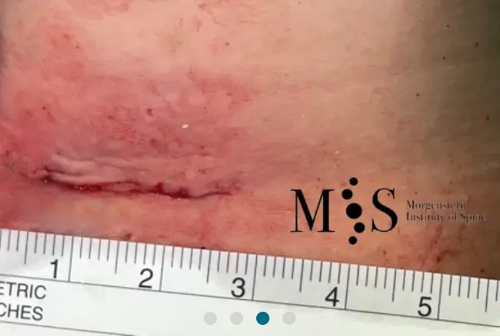
A small skin incision at the patient’s throat after endoscopic anterior fusion surgery of the
cervical spine (endoACDF) with placement of two interbody cages using this small skin incision
.
Endoscopic ACDF starts with an endoscopic discectomy to decompress neural structures, like the spinal cord, and prepare the disk for the cage placement. Once the interbody cervical disk has been prepared, the an interbody device is percutaneously placed into the disk. This device can either be a titanium interbody cage to achieve vertebral fusion or a disk prothesis that allows to restore movement in the cervical spine. The placement of the device is done unter x-ray fluoroscopic control and direct endoscopic vision, see the animation on the figure at the right side of this page.
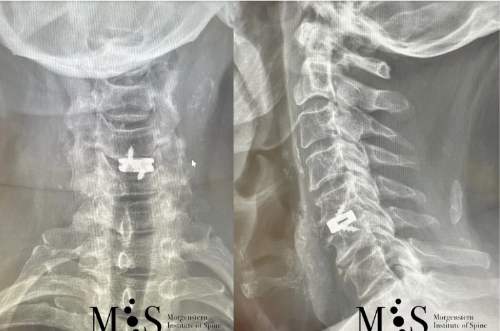
X-ray in A/P (left figure) and lateral (right figure) figures of a titanium
interbody cage placed at level C5/C6 with endoscopic surgery
Radiating pain in the arms usually completely recedes and the patient can start walking just a few hours after surgery and hospital discharge in less than 24 hours after surgery.
Clinical case example
This 49 years-old patient presented with a migrated cervical herniation at level C4/C5 and an unstable disk at C5/C6. En endoscopic cervical decompression was performed to remove the herniation and two intervertebral cages were placed endoscopically using a a skin incision of just 2 cm length. Post-operatively, the patient recovered very quickly and was discharged from the hospital within a day after surgery.
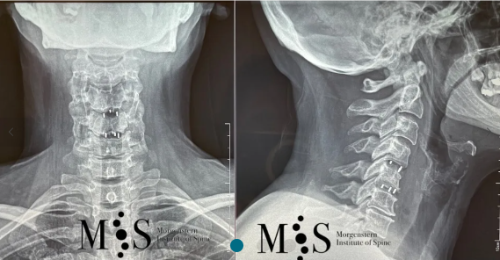
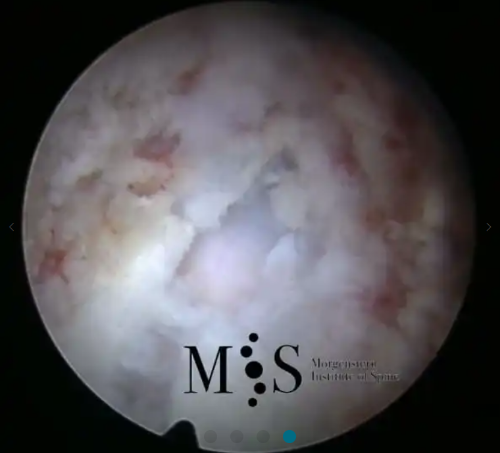
Images showing the endoscopic placement of a cage into a cervical disk
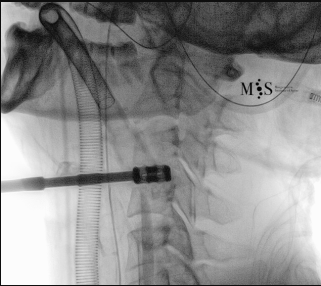
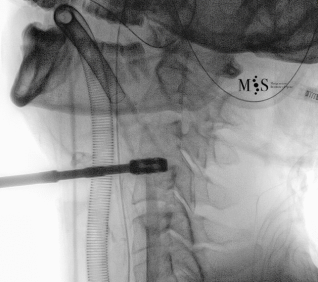
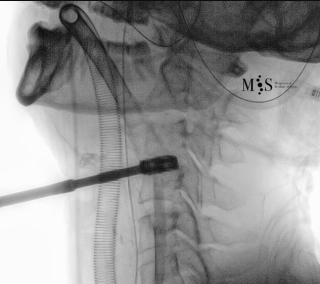
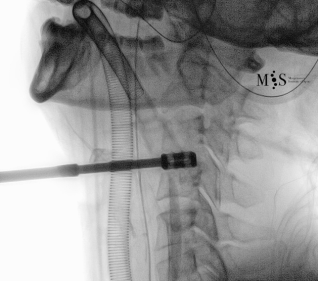
Animated image showing the endoscopic insertion of an intervertebral cage into a cervical disk.
Note the distraction of the disk space during as the cage is inserted.
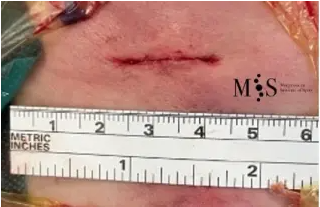
Minimal skin incision of only 2 cm length after the placemente of 2 cervical
intervertebral cages in the cervica spine using the endoscopic fusion technique
| Morning | Afternoon | |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |
| Tuesday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |
| Wednesday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |
| Thursday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |
| Friday | 9.00 - 15.00 h | - |