Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknon- Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari General de Catalunyaen/health-centers/hospital-universitari-general-catalunya
 Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
Centro Médico Teknonen/health-centers/centro-medico-teknonHospital Universitari Sagrat Coren/health-centers/hospital-universitari-sagrat-cor
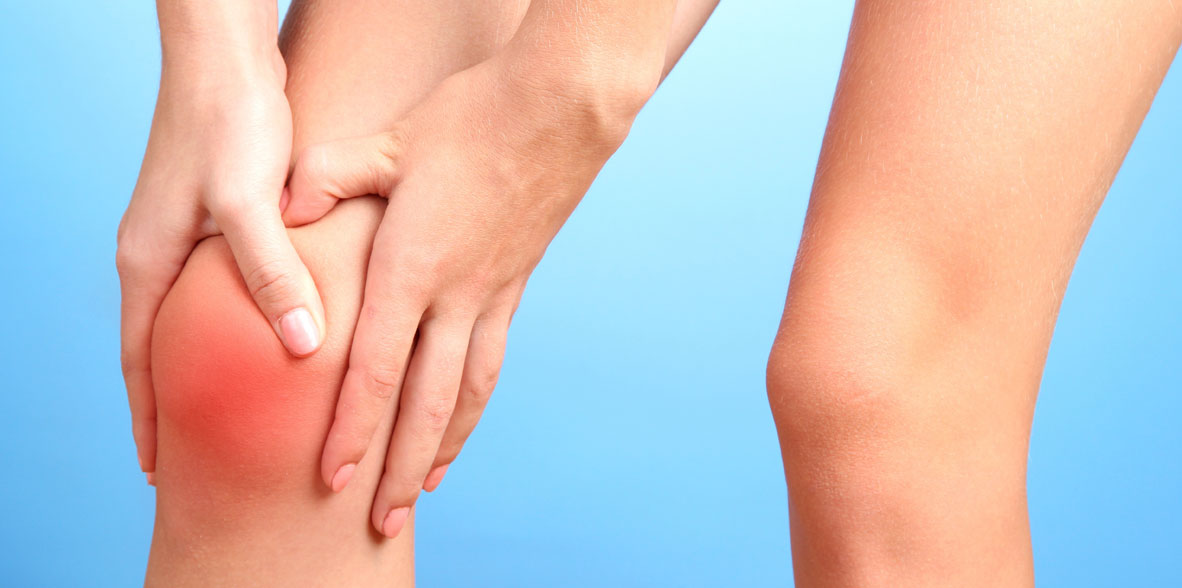
Glucosamine is a compound found naturally in the body, especially in the fluid around the joints. It has been studied as a dietary supplement for the management of osteoarthritis, focusing primarily on its potential to relieve symptoms and improve joint health.
Research into the effectiveness of glucosamine for osteoarthritis has yielded mixed results. Some studies have shown modest benefits in reducing pain and improving joint function, especially in individuals with mild to moderate osteoarthritis.
Glucosamine is sometimes used as part of a comprehensive osteoarthritis treatment approach to help relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function.
Some people with osteoarthritis may experience relief from pain and stiffness, as well as improved mobility with glucosamine supplementation, especially when combined with other therapeutic approaches such as exercise and weight reduction.
Typical doses of glucosamine used in clinical trials for osteoarthritis range from 1000 to 1500 mg per day, usually in divided doses. It is important to follow the dosage instructions recommended by your doctor.
Glucosamine supplementation is usually long-term, as it may take several weeks or months to see significant benefits on osteoarthritis symptoms.
People allergic to shellfish should use glucosamine supplements derived from non-marine sources.
Glucosamine may interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners and diabetes medications, so it is important to discuss its use with your doctor, especially if you have other medical conditions or are taking any medications.